Con-API’s LLMs & NLP Research
Leveraging language models and natural language processing to automate construction knowledge extraction and processing.
Con-API’s automation capacity is primarily founded in Large Language Models (LLMs) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) which can make complex construction information searchable, analyzable, and actionable. From parsing safety regulations to validating design specifications, we develop systems that combine domain-specific subjects with AI language understanding, reducing human workload while improving consistency and efficiency in construction documentation.
Research themes:
- Specification and compliance checking using NLP
- Automated extraction of inspection items from construction documents
- Integration of LLMs into visual-language systems for safety monitoring
- BIM and NLP for automated schedule management
- AI ethics and trustworthy deployment in AEC
Featured Representative Works
1. Tsai, W. L., Le, P. L., Ho, W. F., Chi, N. W., Lin, J. J.*, Tang, S., & Hsieh, S. H. (2025). Construction safety inspection with contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP) image captioning and attention. Automation in Construction, 169, 105863. (SCI) ❐

The developed mobile application preview from Figure 4 and The attention map with generated captions predicted by the model during testing from Table 7.
This study introduces an AI-powered safety inspection framework that utilizes contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP) and attention mapping to automate the detection and description of unsafe site conditions from images. A mobile application is then programmed to package the entire framework into a single process, improving site inspection efficiency.
First, A CLIP model is first fine-tuned to produce CLIP embedded images and attributes. Then, a prefix captioning pipeline then concatenates the caption, attribute, and image embeddings of the input image. Finally, a GPT-2 Language model can then automatically generate safety observations from construction site image. By fine-tuning CLIP for nine distinct violation categories, the system achieves 73.7% average classification accuracy, outperforming baseline methods by over 40%.
The resulting mobile application allows inspectors to quickly capture images, receive AI-generated violation captions, and compile safety reports. User feedback suggests that the app streamlines inspections, reduces reporting time, and improves documentation quality.
2. Singh, A. K., A. Pal, P. Kumar, Lin, J. J., and S. H. Hsieh (2023). “Prospects of Integrating BIM and NLP for Automatic Construction Schedule Management,” Proceedings of the 40th International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction (ISARC 2023), July 4-7, 2023, Chennai, India, 238-245. (IAARC) ❐
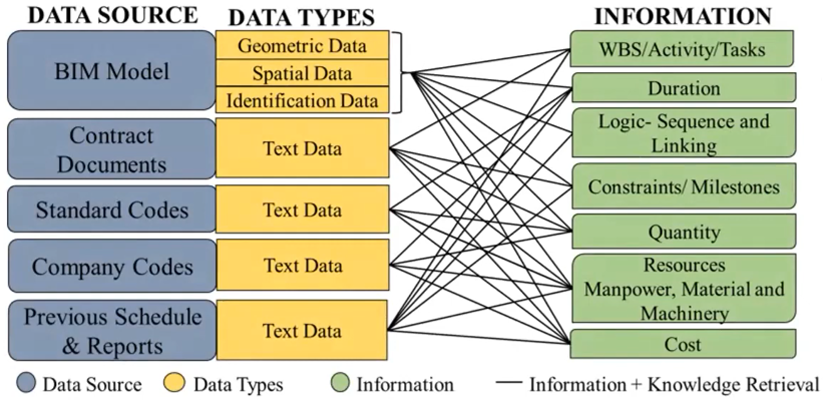
From Figure 2: The mapping between the collected construction documents/model data and the
information requirements for automated Construction Schedule Management.
This paper reviews the potential of integrating Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Building Information Modeling (BIM) to transform how construction schedules can be created and updated automatically. Traditional scheduling is largely manual, making it time-consuming, error-prone, and inconsistent.
The authors survey of state-of-the-art research to explore how NLP can automatically extract and interpret schedule-relevant information from project documents, BIM models, and historical data. There is an emphasis on the structural and visual context from BIM models which can greatly support automated updates. The paper presents a generalized NLP data processing workflow, identifies key challenges in real-world adoption, and proposes three future research directions for integrating BIM and NLP in construction schedule management.
By bridging unstructured text data with structured model-based information, this approach could potentially enable automated, data-driven scheduling. The implementation can reduce human workload and improving planning accuracy.
Conference Highlights
Lin, Z. J., and Lin, J. J. (2023). Automated Alignment Between Issue Tracking Items and Schedule Activities Using Rule-based and Learning Approaches. The 27th Conference on Construction Engineering and Management, July 13, Hsinchu, Taiwan (pp. 113).
Wu, Y.R., Chuang K.Y., Lin, J. J. and H.P. Tserng (2021). “Incorporating lean principles into ISO19650 for information management in turnkey projects,” Proceedings of the 25th Symposium on Construction Engineering and Management, Paper No. 120, July 16, 2021, Taipei, Taiwan.
Project Involvement within this field
以語意分析模型檢驗工程設計成果一致性
Examine the consistency of engineering design with semantic analysis models.
2022.Feb – 2023.Feb. PI
Sponsor: Sinotech Engineering Consultant
以自然語言處理擷取施工規範查驗項目並輔助查驗表單的設計與檢核
Employing natural language processing to capture construction specification inspection items and assist in the design and verification of inspection forms.
2023.Jun – 2024.Jun. Co-PI
Sponsor: National Science and Technology Council (NSTC)
